Operation scenarios
This document describes how to use open-source SDK to send and receive messages using the SDK for Java as an example and helps you better understand the message sending and receiving processes.
Prerequisites
Operation step
Step 1. Install the Java dependency library
Add the following dependencies to pom.xml:
<!-- in your <dependencies> block --><dependency><groupId>com.rabbitmq</groupId><artifactId>amqp-client</artifactId><version>5.13.0</version></dependency>
Step 2. Produce a message
Compile and run MessageProducer.java.
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;import com.tencent.tdmq.demo.cloud.Constant;/*** Message producer*/public class MessageProducer {/*** Exchange name*/private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "exchange_name";public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// Connection factoryConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();// Set the service address (replace with the access point address copied in the console)factory.setUri("amqp://***");// Set virtual hosts (copy the complete vhost name from the open-source RabbitMQ console)factory.setVirtualHost(VHOST_NAME);// Set the username (user name in the permission configuration of the vhost in the open-source RabbitMQ console)factory.setUsername(USERNAME);// Set the password (key for the corresponding user)factory.setPassword("****");// Get the connection address and establish the channeltry (Connection connection = factory.newConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel()) {// Bind the message exchange (EXCHANGE_NAMEmust exist in the TDMQ for RabbitMQ console, and the exchange type must be the same as that in the console)channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "fanout");for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {String message = "this is rabbitmq message " + i;// Publish a message to the exchange, which will automatically deliver the message to the corresponding queuechannel.basicPublish(EXCHANGE_NAME, "", null, message.getBytes());System.out.println(" [producer] Sent '" + message + "'");}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
Parameter | Description |
EXCHANGE_NAME | Exchange name, which can be obtained from the exchange list in the console. |
factory.setUri | Cluster access address, obtained from the Client Access section on the cluster basic information page. 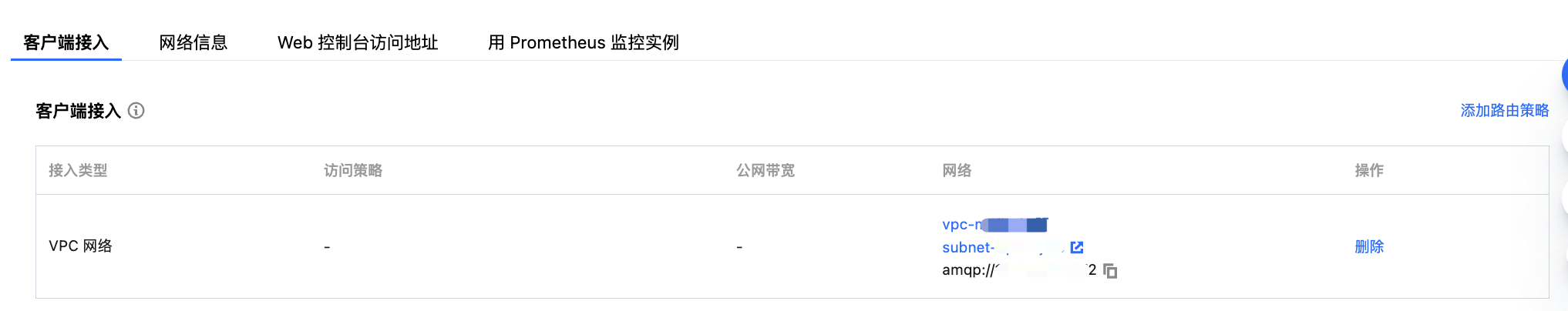 |
factory.setVirtualHost | Vhost name, obtained from the Vhost list in the console. |
factory.setUsername | Username, as created in the console. |
factory.setPassword | User password, as set when creating the user in the console. |
Step 3. Consume the message
Compile and run MessageConsumer.java.
import com.rabbitmq.client.AMQP;import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;import com.rabbitmq.client.DefaultConsumer;import com.rabbitmq.client.Envelope;import com.tencent.tdmq.demo.cloud.Constant;import java.io.IOException;import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;/*** Message consumer*/public class MessageConsumer1 {/*** Queue name*/public static final String QUEUE_NAME = "queue_name";/*** Exchange name*/private static final String EXCHANGE_NAME = "exchange_name";public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// Connection factoryConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();// Set the service address (replace with the access point address copied in the console)factory.setUri("amqp://***");// Set virtual hosts (copy the complete vhost name from the open-source RabbitMQ console)factory.setVirtualHost(VHOST_NAME);// Set the username (user name in the permission configuration of the vhost in the open-source RabbitMQ console)factory.setUsername(USERNAME);// Set the password (key for the corresponding user)factory.setPassword("****");// Get the connection addressConnection connection = factory.newConnection();// Establish a channelChannel channel = connection.createChannel();// Bind the message exchangechannel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "fanout");// Declare the queue messagechannel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, true, false, false, null);// Bind the message exchange (EXCHANGE_NAMEmust exist in the TDMQ for RabbitMQ console, and the exchange type must be the same as that in the console)channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "");System.out.println(" [Consumer1] Waiting for messages.");// Subscribe to the messagechannel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, false, "ConsumerTag", new DefaultConsumer(channel) {@Overridepublic void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope,AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body)throws IOException {// Process received messages with business logic.System.out.println("Received: " + new String(body, StandardCharsets.UTF_8) + ", deliveryTag: " + envelope.getDeliveryTag() + ", messageId: " + properties.getMessageId());channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(), false);}});}}
Parameter | Description |
QUEUE_NAME | Queue name, which can be obtained from the queue list in the console. |
EXCHANGE_NAME | Exchange name, which can be obtained from the exchange list in the console. |
factory.setUri | Cluster access address, obtained from the Client Access section on the cluster basic information page. 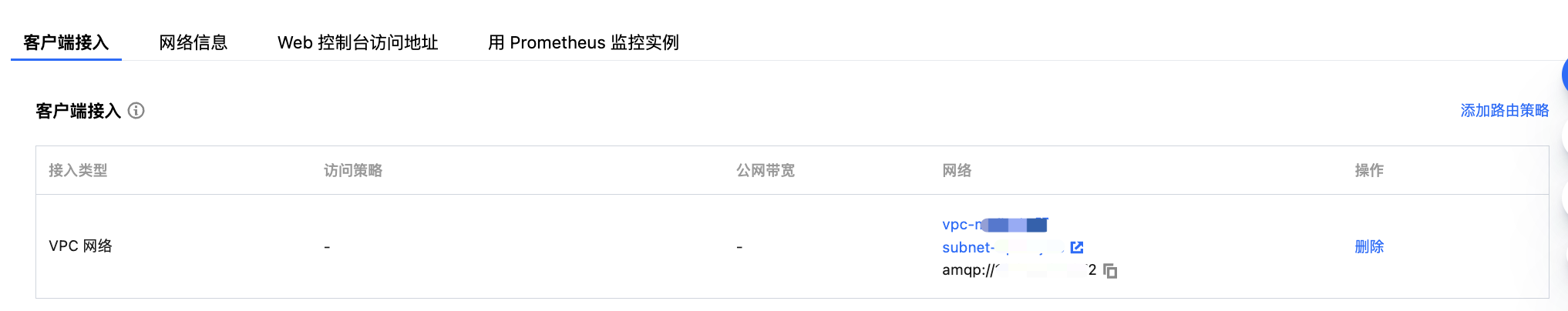 |
factory.setVirtualHost | Vhost name, obtained from the Vhost list in the console. |
factory.setUsername | Username, as created in the console. |
factory.setPassword | User password, as set when creating the user in the console. |