安全规则为云数据库与云存储中的数据提供强大的、完全可自定义的保护。您可以按照本指南中的步骤轻松开始使用规则,确保数据安全,并保护您的应用免受恶意用户攻击。
了解安全规则语言
安全规则语言使用一种 JSON 结构,key 指代操作类型,value 为允许操作时的条件,可以为 boolean 或表达式字符串,表达式字符串语法类似 Javascript 语言,其是单个逻辑表达式,或多个逻辑表达式通过与/或方式组合,当表达式的计算值决定了操作是否被允许。
步骤1:定义规则和数据结构
安全规则提供了内部变量获取请求数据的内容以根据数据进行访问控制,数据的组织方式可能会影响规则的写法,例如,论坛应用中需要限制所有登录用户可以浏览内容,用户只能修改、删除自己的帖子,那么论坛帖集合(posts)中记录需要存储 userID 表示记录归属,安全规则根据 userID 字段限制 update 与 delete 行为,放过所有的登录用户的 read 行为。
步骤2:获取安全规则
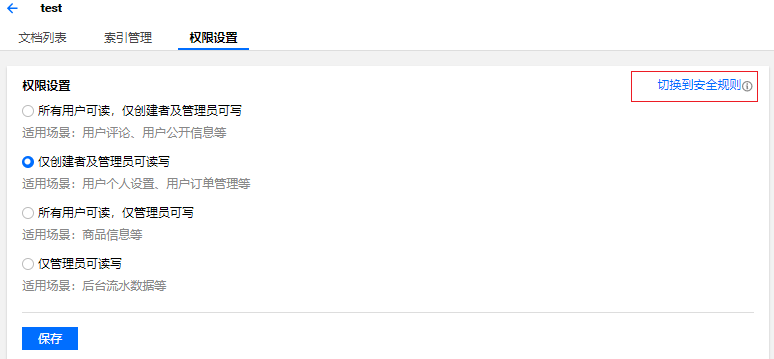
1. 以云数据库集合权限管理为例,进入控制台,选择对应环境,单击左侧菜单栏数据库查看环境下 云数据库集合 的详情信息。
2. 单击集合名称,在详情中切换至权限设置页面,可由基础权限控制选择切换为安全规则。

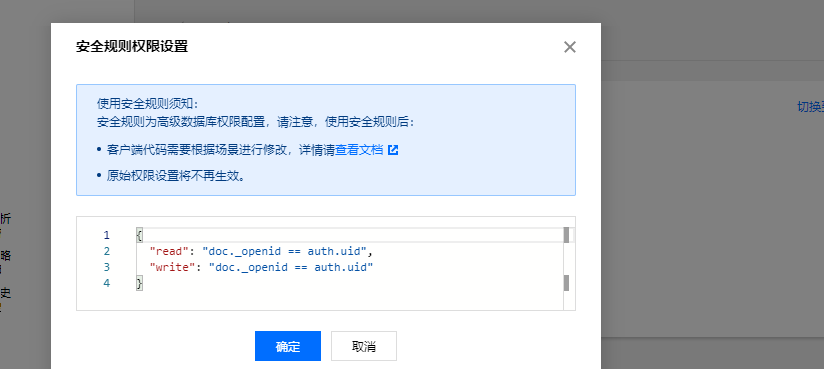
3. 单击切换到安全规则,系统会根据已有的基础权限转化为对应的安全规则信息,开发者也可在其基础上进行修改。

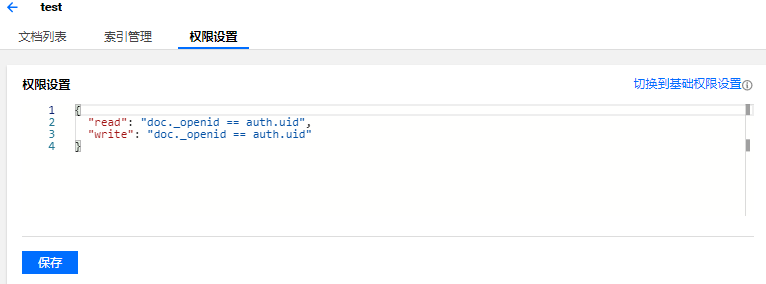
4. 已经设置成功,正在使用的安全规则后续可以在权限设置中进行查看及修改。

步骤3:编辑发布安全规则
在云开发控制台权限控制页中可编辑所需的安全规则,例如上述论坛应用的例子,可改 posts 集合的权限为以下规则:
{"read": "auth != null", // 所有登录用户可读"create": "auth != null", // 所有登录用户可以发帖"update": "doc.userID == auth.openid", // 用户只能修改自己的帖子"delete": "doc.userID == auth.openid" // 用户只能删除自己的帖子}
通过保存按鈕使编辑的新规则部署云端,保存成功后安全规则即时生效。