计算加速套件 TACO Kit(TencentCloud Accelerated Computing Optimization Kit)是一种异构计算加速软件服务,具备领先的 GPU 共享技术和 GPU 在离线混部能力,搭配腾讯自研的软硬件协同优化组件和硬件厂商特有优化方案,支持物理机、云服务器、容器等产品的计算加速、AI 训练及推理加速等各个应用场景,帮助用户实现全方位全场景的降本增效。
同时,TACO Kit 立足于腾讯丰富的AI业务场景, 专注于生成式 AI 的核心技术优化,包括训练框架优化、推理性能优化以及网络通信优化。通过这一整套高效的 AI 加速解决方案,TACO Kit 为客户提供涵盖文生文、文生图、文生视频、图生文、音生文等多个跨模态领域的AI加速能力,助力客户 AI 业务创新。
其架构示意图如下所示:
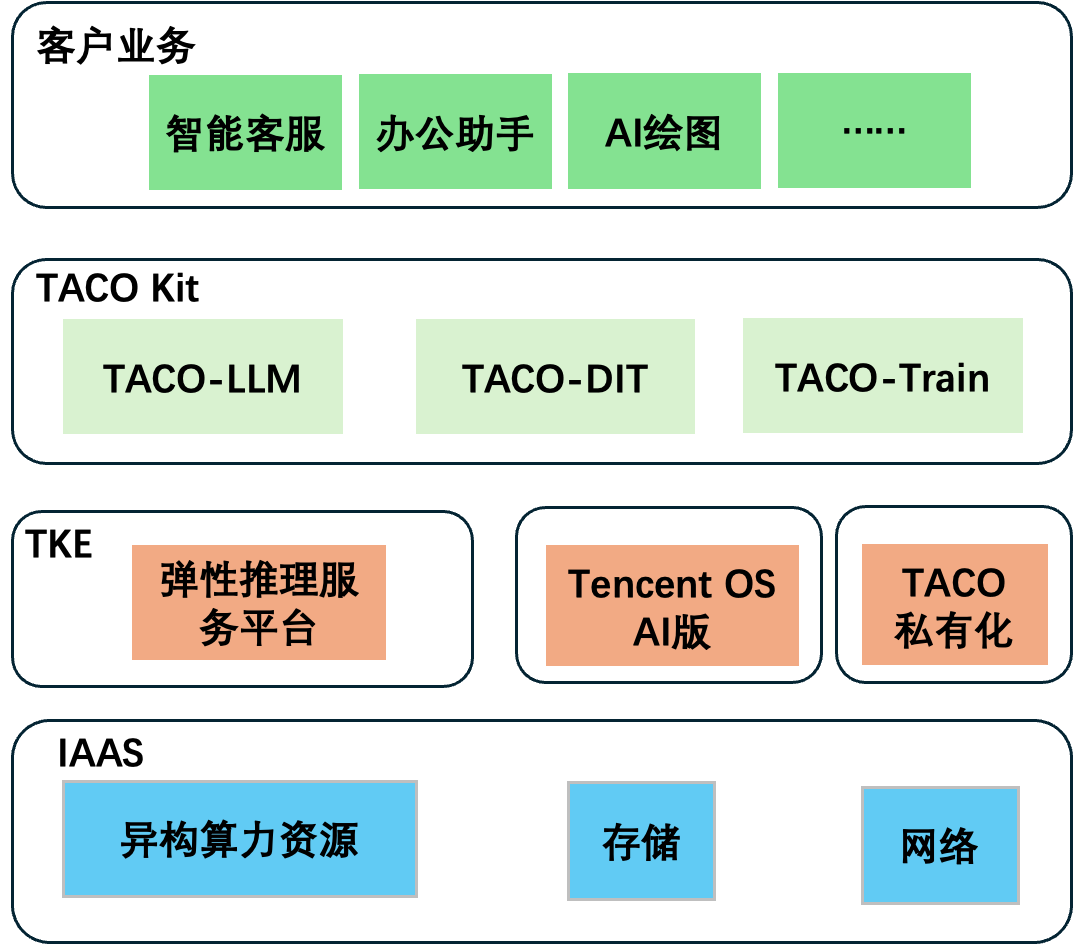
您可通过以下文档,了解更多关于 TACO Kit 各个加速组件的信息: